This post can also be viewed at:
![]() Danish
Danish
Brute-force attacks are a persistent security threat that has evolved over the years as technology advances. In this article, you will learn what a brute force attack is, the attack methods and variations, and prevention strategies you can use to protect your data.
What is a brute force attack?
A brute force attack is a type of cyberattack in which an attacker attempts to gain access to a computer system or network by guessing a password or personal identification number (PIN). Sometimes an attacker can use automated software to make guesses easier and faster.
all brute force attack They are also called cryptanalysis attacks because they rely on cryptographic capabilities to crack passwords and penetrate systems.
A brute force attack can be very successful if the attacker has sufficient time and computing resources. However, they are very difficult to execute and usually take a long time to complete. Therefore, they are not generally used by attackers except in very specific circumstances.
How do brute force attacks work?
Many people think that BFA is crude, rudimentary, and rough. Couldn’t be further from the truth. They rely heavily on passwords and password dictionaries and cryptographic ‘magic’ that allows malicious actors to guess users’ credentials.
Brute-force attacks usually follow a general pattern. That is, an attacker will attempt to log in to a user account using different user name and password combinations until the correct one is found. If successful, the attacker can gain access to the victim’s account and data.
Brute force attacks can be done both online and offline. Online brute force attacks occur when an attacker has direct access to a victim’s system, whereas offline brute force attacks occur when an attacker tries to guess a password from a compromised database.
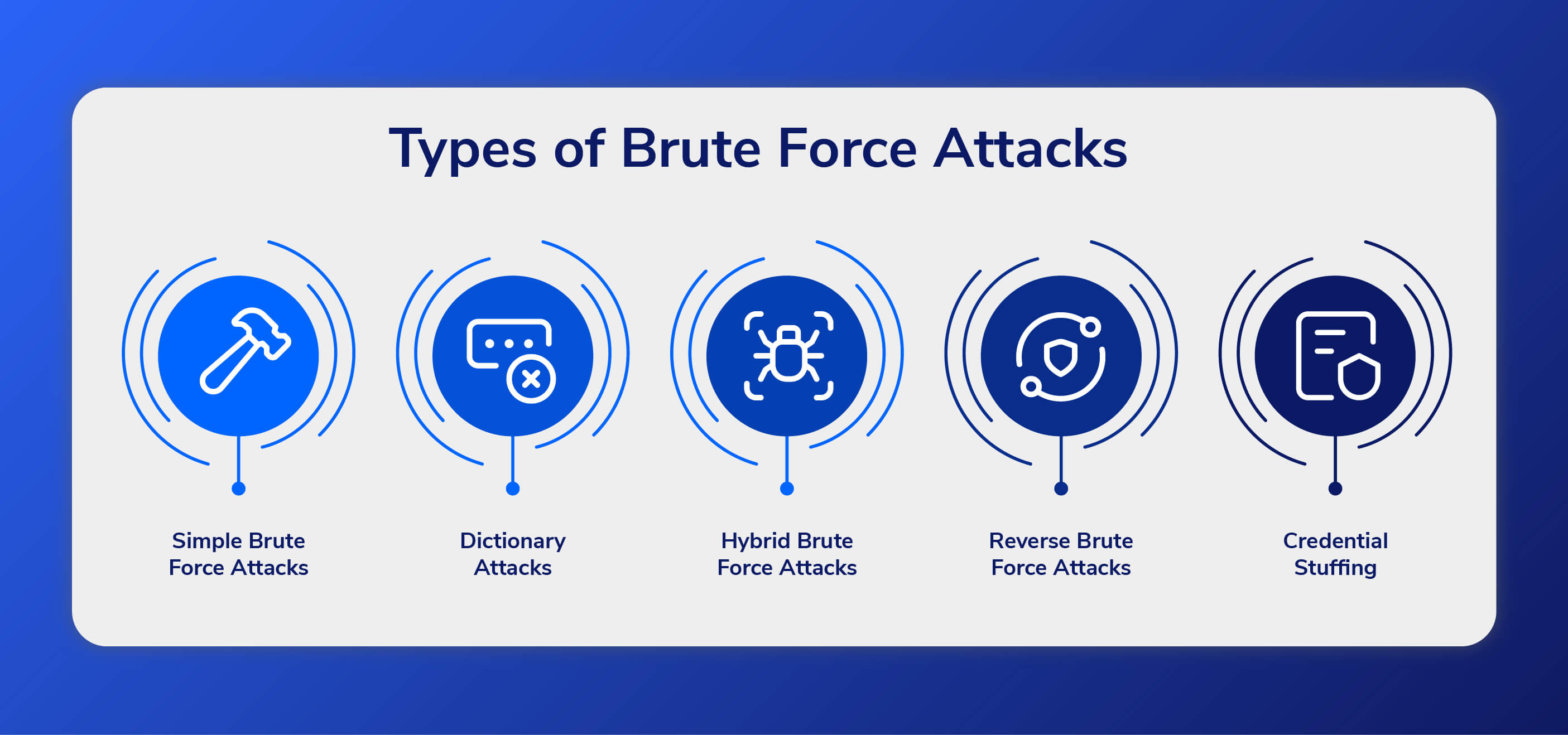
Brute force attack types
There are several types of brute force attacks, each with its own goals and methods.
simple brute force attack
This type of attack tries all possible character combinations to guess the password. This can be a very time-consuming process, but modern computing power makes it feasible for attackers.
dictionary attack
This is the most common type of brute force attack in which an attacker takes a list of commonly used passwords and tries to guess them.
Dictionary attacks are so named because they involve hackers looking through a dictionary and replacing words with symbols and numbers. Compared to more recent and more successful attack strategies, these types of attacks are usually time consuming and relatively less successful.
Hybrid brute force attack
A hybrid brute force attack occurs when a hacker uses both a dictionary attack method and a simple brute force attack. Once a hacker has your username, they can use dictionary attacks and simple brute force techniques to find your account login information.
Attackers start with a list of potential words and then experiment with letters, letter and number combinations to find the right password. This approach allows hackers to discover passwords that combine common or popular words such as “SanFrancisco123” or “Toyota2020” with numbers, years, or random characters.
reverse brute force attack
A reverse brute force attack is when an attacker uses a known password or pattern and tries to find a username or account number to gain access to the system. This contrasts with traditional brute force attacks, in which an attacker tries various combinations of characters to guess a password.
credential stuffing
all credential stuffing The attack uses stolen login credentials from numerous websites. Credential stuffing works because people frequently reuse login names and passwords. As a result, if a hacker is able to access a person’s account, for example at an online store, they are more likely to grant access to that person’s online bank account with the same credentials.
Another classification is that of long-lived versus distributed brute-force attacks.
long term brute force attack
The target machine will be under attack for an extended period of time. This can vary from days to weeks depending on user pass pair strength, pair length, calculation speed, code cracking methods and countermeasures. BFA studies have shown that a single system can withstand 50 to 100 brute-force attacks per day. Access requests can also originate from more than one IP address. Long term brute force attacks are more likely to be detected.
Distributed brute force attack
In the case of a distributed brute force attack, the login attempts are in the form of short, very ‘focused’ bursts (e.g. 40 login attacks launched from a single IP, spread out over 3-4 minutes). Conclusion: Decreased detection rate and increased chance of success.
Prevent brute force attacks
To prevent brute force attacks, it is important to use strong passwords that are difficult to guess. Avoid using easily guessable words such as your name or birthday. Instead, use a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
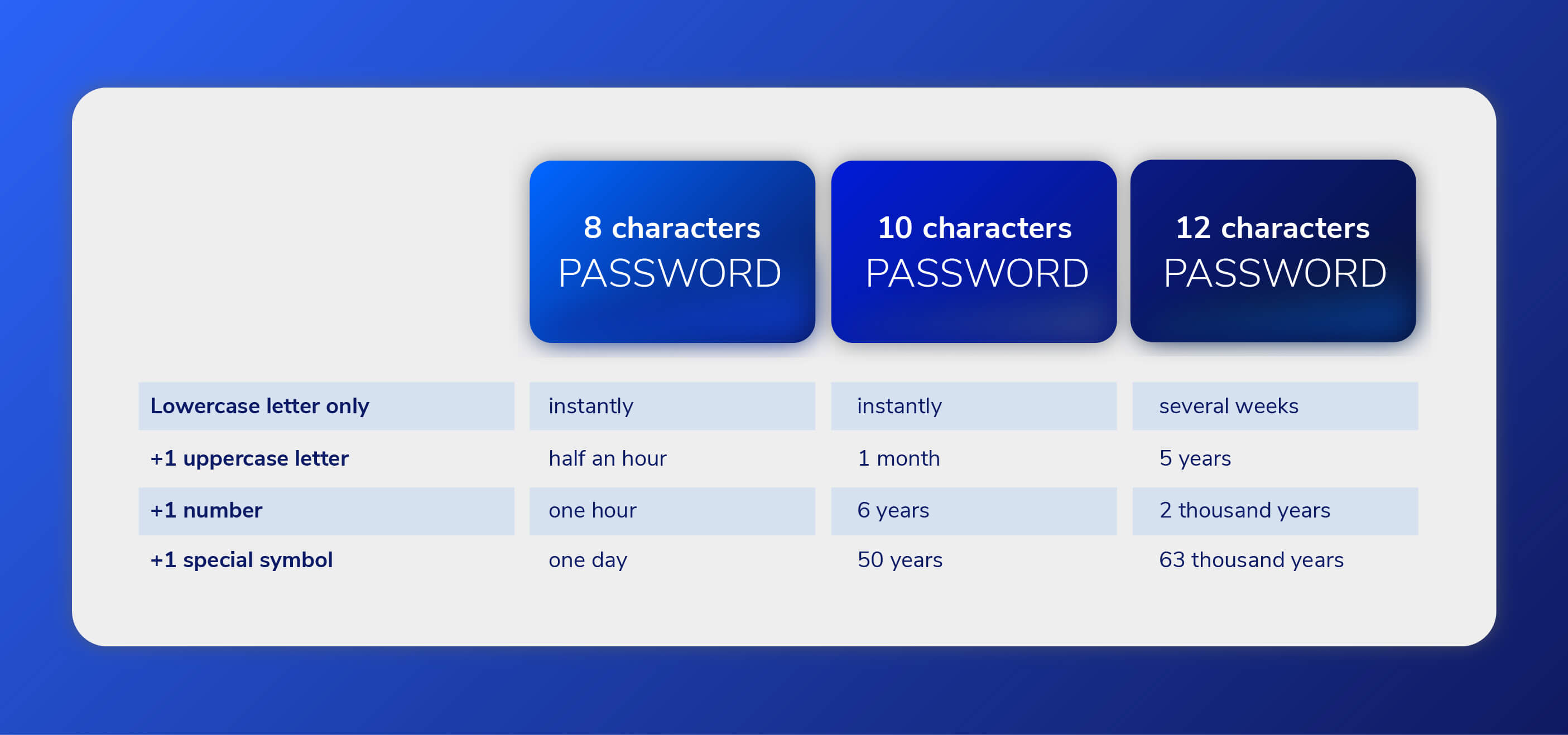
Another prevention strategy is to limit the rate of login attempts so that attackers cannot keep trying different passwords. You can also apply account lockout policies so that accounts are automatically locked after a certain number of failed login attempts.
two-factor authentication Even if an attacker knows the correct username and password, logging in requires access to a second factor (usually a physical token or code sent via SMS), which can make brute force attacks much more difficult.
What else can you do?
Enable Network Level Authentication
NLA adds an extra layer of protection by requiring users to authenticate themselves before starting a session. To do so, open Control Panel, go to System and Security, and click on System.
Go to Remote Settings, click Remote, then click Remote Desktop. Highlight the “Allow connections only from computers running Remote Desktop with Network Level Authentication” option.
Manually block TCP port 3389
Go to Control Panel, select System and Security, and click Windows Firewall. Go to Advanced Settings >> Inbound Rules, click New Rule, then select Port. When finished, click Next. Highlight TCP, then select a specific local port. Enter 3389. Click Next, enter a name for the newly created rule, then click Finish.
Enforcing 2FA on RDP requests
You can enforce two-factor authentication for RDP connections using tokens. quote Microsoft’s documentation on 2FA Rule enforcement for setup and configuration.
Determine if an endpoint has been subjected to a brute force attack
According to Microsoft, computers that have been attacked and/or compromised as a result of a brute force attack have telltale signs. Signs to watch out for include:
- Time and day of the week when login and RDP connection failed
- When to log in successfully after failed attempts
- Event ID 4625 Login Type (Filtered by Network and Remote Interactive)
- Event ID 4625 Reason for failure (filtered by %%2308, %%2312, %%2313);
- The cumulative number of unique user names that failed to log in successfully.
- Number of failed logins (and cumulative)
- Number of RDP inbound external IPs (and cumulative number)
- The number of other systems with RDP inbound connections from one or more of the same IP.
via Microsoft security blog
How can Heimdal® help?
Heimdal’s next-generation antivirus and MDM Anti-Brute-Force The enterprise module can create blocking rules for vulnerable ports and isolate affected systems to protect them from brute force attacks.
This is especially useful for companies acquiring our NGAV solution or any service that includes this module. EDR or XDR software.
Heimdall’s Next-generation endpoint antivirus‘s existing firewall features, such as port and application management, are used together with unique features to ensure brute force and ransomware protection and device isolation.
You can also choose to automatically block RDP ports upon detection of a brute force attack from the unified and intuitive Heimdal dashboard. You also have the option of isolating endpoints. In this case all external connections are routed back through the Heimdal system.
Morten KeesgardHeimdall CEO

A simple standalone security solution is no longer sufficient.
An innovative and enhanced multi-layered EDR security approach to organizational defense.
- Next-generation antivirus and firewall that blocks known threats
- DNS traffic filter to block unknown threats;
- Automatic patching for software and apps without disruption
- Privileged Access Management and Application Control, all from one unified dashboard
last thoughts
In summary, a brute force attack is a cyberattack designed to guess passwords and other credentials by trying different combinations, usually with the help of automated scripts.
These attacks can be damaging because they often go unnoticed as the script continues to work in the background. Fortunately, there are a number of prevention strategies, such as setting up two-factor authentication and implementing complex password policies that can greatly reduce the risk of falling victim to this type of attack.
P.S. Did you enjoy this article? follow us LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook, Youtube, or Instagram To stay up to date on everything we post!
